Introduction to Recursive Function in JavaScript
Javascript is an interpreter and a high-level scripting language that forms the basis of HTML and web-based programming language. A recursive function is the one that calls itself in order to generate an expected output. For easier understanding, you can think of a number function factor, which can be cited as the perfect example of a recursion function in Javascript. In this topic, we are going to learn about the Recursive Function in JavaScript.
Recursion is also defined as the programming pattern, which is often useful in cases where a particular case or task can be easily split into several smaller sub-tasks, which are specifically of the same kind but, of course, much simpler in nature. Whenever a function performs a particular task, it can call many functions as intermediates to process, and when it does to itself, it is called a recursive function.
Syntax of Recursive Function
function func_name(var1,var2) {
//variable declaration
// code block and actual logic
for (initialisation; condition)
}
//loop code block and returning the result
}
//recursively calling a function
func_name(num1, num2)Explanation
- In the syntax explained above, we have tried to understand the concept of recursive functions in Javascript by making use of for looping construct. In the beginning, we have declared a function by the name of func_name, which forms our basic entity, and all the following code will be written inside that function block.
- Next, in the function name, we pass two parameters by the names of var1 and var2, which explains the variables and their values. After that comes the variable declaration part, where we will write the variables and other values required for our code logic and post that the actual code logic will be implemented.
- In this case, we are making use of for loop to write our code logic block. Once the code has been written, there becomes a need to reiterate that function statement, i.e. recursively call that function block which is func_name in this case and therefore, we will be passing two number argument values as parameters in the func_name outside the for loop such that the function is called again until and unless the values passed are consumed.
- This is how a recursion function is implemented in JavaScript. One point to be noted here is that we are not making use of iterative condition in for loop as that condition will be catered by the recursive function in its call.
How Recursive function works in JavaScript?
As JavaScript is a web-oriented language, the recursive function can be implemented by making use of for loop or by while loop. In the case of a recursive function, the program’s main aim is to diminish the major task into many smaller sub-tasks until the subtask fails to comply with the condition and fails to enter inside the loop or any code block written inside the function. It is not necessary that any looping statement has to be used for implementing recursion, but it can also be done by making use of conditional blocks of statements such as if-else constructs.
Examples of Recursive Function in JavaScript
Let us understand this with the help of various examples.
Example #1
Let us understand this with the pow function, which is the shorthand form for power. In this example, we will be reading about pow(a,b), which raises the power of a to the natural number of b. if you speak in other terms, it means that a is to be multiplied by itself b number of times.
//declaration of function power
function pow(a,b) {
//writing if condition and checking if it has broken into simplest task already
if (b == 1) {
//returning the value which needs to be reiterated
return a;
} else {
return a * pow(a, b - 1);
}
}
//recursively calling the function pow by passing two values to process
alert( pow(2, 3) );Output:

In this example, we recursively call the function pow and calculate the power of 2, 3 times which should produce the result 8. When pow is called, the execution block is split into two categories based on conditional statements. The first one will talk about the if statement where if a==1 = b, and the second refers to the else part of the block where a is multiplied by the resultant of the power of a and b-1.
Example #2
In this second example, we will study another very popular example of the recursive function. It is known as finding the factorial of a number. When you talk about finding the factorial of a number, you mean multiplying the number and all the subsequent decreasing values of it till 1.
The snippet formula for finding a number’s factorial is:
b! = 1 iff b=0
else if (b-1)! *b iff b>0Let us try to understand this formula with the help of an example. The factorial of 4 is 4*3*2*1= 24.
Code:
//declaring a function func
function fact(b) {
//declaring a variable
var res = 1;
//for loop to find the factorial of the number
for (let i = b; i > 1; i--) {
//fetching and consolidating the result statement
res *= i;
}
//returning the result which contains the factorial of the number b
return res;
}Output:
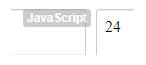
In the code explained above, the factorial would be taken out of any value which is passed inside the function named fact, and the value res will be responsible for calculating the value.
Example #3
In this example, we will see how the recursion function is used in the implementation of counters by making use of the if-else loop.
Code:
//declaring a function value
var Cdown = function(val) {
//checking if the value is greater than 0
if (val > 0) {
//documenting and logging the console output
console.log(val);
return Cdown(val - 1);
} else {
return val;
}
};
Cdown(5);Output:
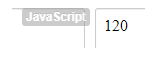
In this example, the value of 5 will be logged as the Cdown function’s output and will calculate the factorial.